Arrange a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Factors Contributing to Lip Filler Migration
Product Formulation
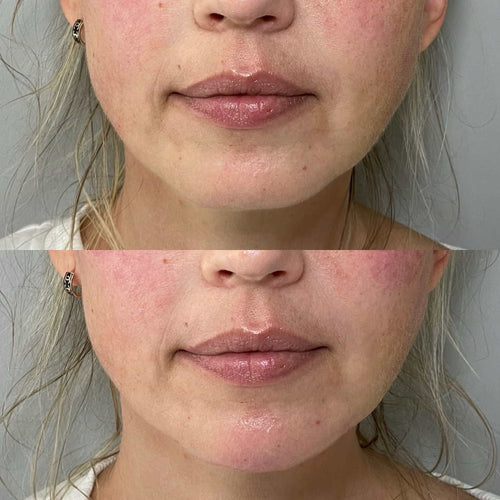
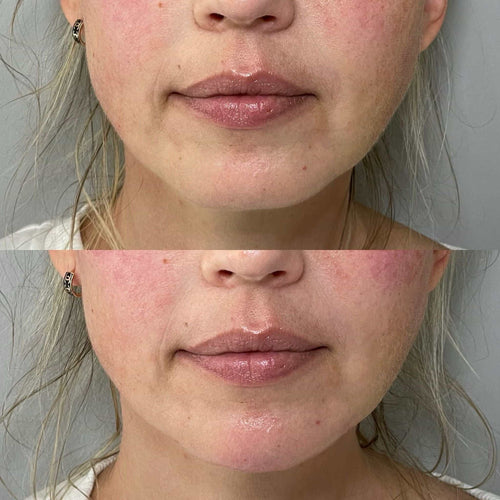
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid (HA) gel, the primary ingredient in most dermal fillers, moves from its original injection site. This can result in an unnatural or asymmetrical appearance, lumps, and distorted lip contours.
Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
1. Injectable Technique:
Improper injection technique is a major culprit. Injecting too deeply or superficially can cause the filler to spread outside the intended area. Incorrect placement, such as placing filler in areas with high movement or thin skin, also increases the risk of migration.
2. Product Formulation:
The size and concentration of HA molecules play a role. Smaller particles are more likely to migrate than larger ones. Similarly, fillers with higher concentrations may be more prone to spreading. Additionally, the cross-linking density (how tightly the HA molecules are bound together) affects stability. Less cross-linked fillers tend to be more fluid and thus more susceptible to migration.
3. Patient Factors:
Certain patient characteristics can influence filler movement. Lip anatomy, such as thin skin or prominent blood vessels, can increase the likelihood of migration. Smoking and sun exposure can also damage collagen and elastin fibers in the lips, compromising their structure and making them more vulnerable to filler displacement.
4. Post-Treatment Activity:
Engaging in strenuous activities or facial massage shortly after treatment can disrupt the gel placement and contribute to migration.
5. Body Movement:
Even normal daily movements, particularly those involving facial expressions and chewing, can cause gradual filler migration over time. This is especially true for areas with high muscle activity, like the lips.
Understanding these factors is crucial for both patients and practitioners to minimize the risk of lip filler migration and achieve optimal aesthetic results.
Injection Technique
Lip filler migration, or the movement of hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers from their intended location, can occur due to a combination of factors related to both the patient and the injection technique.
Patient-related factors include:
• **Lip anatomy:** Individual lip structure and thickness influence filler placement. Thinner lips with less subcutaneous tissue may be more prone to migration as there is less support for the injected material.
• **Smoking:** Smoking constricts blood vessels, affecting circulation and potentially hindering proper integration of the filler.
• **Sun exposure:** Excessive sun exposure can degrade collagen and elastin, weakening the skin’s structure and increasing the risk of filler migration.
• **Certain medical conditions:** Some medical conditions, such as connective tissue disorders, can affect the stability of injected substances.
Injection technique plays a crucial role in minimizing migration:
• **Depth of injection:** Injecting too superficially can lead to fillers sitting on top of the lip tissue and migrating. Proper depth ensures the filler is integrated into the deeper layers for better support.
• **Spread and distribution:** Evenly spreading the filler and avoiding overfilling are essential. Excessive product in one area increases pressure, making migration more likely.
• **Needle technique:** Using a properly calibrated needle with appropriate size and angle can minimize trauma to surrounding tissues, facilitating better integration.
• **Proper patient positioning:** Patient posture can affect filler distribution. Ensuring proper head and neck support can prevent product from shifting during the procedure.
Experience and skill of the injector are paramount in preventing migration. Understanding facial anatomy, mastering injection techniques, and using appropriate products are key to achieving natural-looking results with minimal risk of filler movement.
Individual Anatomy
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid filler, a common substance used to enhance lips, moves from its intended location.
Several factors can contribute to this phenomenon:
- Patient-Related Factors:
- Excessive Movement of the Lips:** Frequently puckering, kissing, or making exaggerated facial expressions soon after injection can push filler out of place.
- Smoking:** Smoking reduces blood flow and can interfere with the body’s natural healing process, potentially increasing migration risk.
- Injection Technique:
- Incorrect Injection Depth:** Placing filler too superficially increases the chance of it moving or migrating.
- Overfilling:** Injecting excessive volume can exceed the lip’s capacity, leading to displacement.
- Filler Product Properties:
- Particle Size:** Smaller hyaluronic acid particles tend to spread more readily and may migrate more easily than larger ones.
- Cross-Linking Density:
Higher cross-linking density generally means the filler is more stable and less prone to migration, but it can also make it more difficult to dissolve if needed. - Individual Anatomy:
- Lip Structure:** Thin lips or those with prominent muscle attachments may have a higher susceptibility to migration due to increased movement and tension.
- Facial Muscle Activity: Highly active facial muscles can exert pressure on filler, leading to displacement.
- Age**: The natural elasticity and collagen levels in the skin decrease with age, making it more susceptible to filler movement.
- Lifestyle**: Activities involving repetitive facial expressions or forceful oral movements, such as playing wind instruments or chewing gum excessively, can increase the risk of migration.
- Filler type**: The specific type and concentration of HA filler used can affect its tendency to migrate.
-
Muscle Contractions:
-
The muscles of the face, particularly those involved in speaking, smiling, and puckering, constantly contract and relax.
-
These movements can cause the injected filler to shift or migrate, especially if it’s not properly dispersed or if the injection technique is inadequate.
-
Filler Placement:
-
The location where filler is injected can influence its susceptibility to migration.
-
Areas with higher muscle activity, such as the cupid’s bow or the center of the lip, are more prone to filler movement.
- Incorrect Injection Technique: Injecting too superficially or at improper angles can increase the likelihood of filler movement.
- Patient Movement During Treatment: Even slight movements during injection can cause the filler to shift.
- Overfilling: Injecting excessive amounts of filler can create pressure that leads to migration.
- Certain Activities After Injection: Engaging in activities such as intense exercise, facial massage, or prolonged sun exposure shortly after treatment can increase the risk of migration.
- Product Type and Viscosity: Some fillers have a higher tendency to migrate than others. Thinner fillers may be more prone to movement compared to thicker, gel-like substances.
- Choose a highly qualified and experienced injector who is well-versed in lip augmentation techniques.
- Clearly communicate your desired outcome to the injector.
- Follow pre-treatment instructions carefully, including avoiding certain medications and activities.
- Remain still and relaxed during the injection procedure.
- Avoid touching or massaging the injected area for several days after treatment.
- Limit strenuous activity, facial expressions, and sun exposure for a week following the procedure.
- Massage Therapy: A qualified injector can gently massage the migrated filler to attempt to reposition it.
- Dissolving Agent (Hyaluronidase):** This enzyme specifically breaks down hyaluronic acid fillers, allowing for removal or re-distribution of the filler.
- Revision Injection:** Additional filler may be strategically injected to balance the asymmetry caused by migration.
- Look for board-certified plastic surgeons or licensed medical professionals with extensive experience in injectables.
- Inquire about their training and certifications in lip augmentation techniques.
- Review before-and-after photos of patients who have undergone similar procedures.
- Consult with multiple injectors to gather different perspectives and ensure you feel comfortable with their approach.
- Incorrect injection technique: Placing filler too superficially or spreading it excessively can increase the risk of migration.
- Excessive volume:** Injecting a large amount of filler can overload the surrounding tissue, making it more susceptible to displacement.
- Patient movement during treatment:** Even subtle movements can cause the filler to shift position. It’s crucial for patients to remain still during injection.
- Certain facial habits: ** Frequently puckering or pressing the lips together can contribute to filler migration over time.
- Natural lip movement and expression:** The lips are constantly in motion, and even with proper placement, some degree of filler migration is possible.
- Choose a qualified injector: ** Look for experienced practitioners who have extensive knowledge of facial anatomy and proper injection techniques.
- Discuss your goals openly: Be honest with your injector about the desired outcome and any concerns you may have.
- Follow pre-treatment instructions: Avoid certain medications or activities before your appointment, as instructed by your injector.
- Remain still during treatment: ** It’s vital to follow your injector’s guidance and minimize movement during the injection process.
- Be mindful of facial habits: Avoid excessive puckering or pressing your lips together after treatment.
- Hyaluronidase enzyme:** This medication can be injected to dissolve the hyaluronic acid gel.
- Manual massage: Gently massaging the affected area may help reposition the filler.
- Repeat injections: * In some cases, additional filler may be injected to restore the desired shape and volume.
The Role of Movement in Lip Filler Migration
Natural Facial Expressions
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid (HA) filler, injected into the lips, moves from its original location to another area of the face. Understanding this phenomenon requires examining the dynamic interplay between facial movement and the properties of HA fillers.
**Facial expressions**, particularly those involving the **orbicularis oris muscle**, which surrounds the mouth, play a significant role in lip filler migration. The orbicularis oris is responsible for movements like smiling, puckering, and kissing. When these muscles contract, they exert pressure on the surrounding tissues, including HA filler.
HA fillers, while designed to be gel-like and stable, are not entirely rigid. Their **molecular structure** allows them to deform and flow under pressure. This means that with repetitive facial expressions, especially forceful ones, the filler can shift from its intended location.
The *depth* at which the filler is injected also influences migration risk. Deeper injections generally have a lower risk because the muscle contractions exert less direct pressure on the filler. However, even deeply placed filler may migrate over time due to the constant micro-movements of the facial muscles.
Other factors that can contribute to lip filler migration include:
Understanding the factors influencing lip filler migration is crucial for both patients and practitioners. Patients should be informed about potential risks and advised on minimizing movement that could cause migration. Practitioners should carefully assess each patient’s facial anatomy, muscle structure, and lifestyle before injecting fillers.
Muscle Activity
Lip filler migration is a common concern for individuals who have undergone lip augmentation procedures. It occurs when hyaluronic acid (HA) filler, injected into the lips, moves from its original placement to other areas.
Several factors contribute to this phenomenon, with muscle activity playing a significant role.
Other contributing factors include:
*
Type of filler used – some HA fillers are formulated to be more resistant to migration than others.
*
Individual patient anatomy and muscle structure – facial muscles vary in size, shape, and strength.
*
Post-injection care – avoiding excessive sun exposure, massage, or facial exercises after treatment can help minimize movement.
Understanding the role of muscle activity in lip filler migration is crucial for practitioners to optimize injection techniques and patient counseling.
Oral Habits
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid (HA) dermal fillers, commonly used to enhance lip volume and shape, move from their intended injection site.
Movement can be influenced by a variety of factors, including facial movements, oral habits, and the type of filler injected.
Understanding the role of movement in lip filler migration is crucial for both patients and practitioners aiming to achieve optimal results and minimize complications.
Facial expressions, such as smiling, frowning, puckering, and talking, involve complex muscle contractions that can displace filler particles.
Repeated or forceful movements over time can contribute to filler migration, particularly along the contours of the lips.
Oral habits, such as sucking on straws, biting nails, and clenching the jaw, exert pressure on the lip area, potentially causing filler to shift or migrate.
These habits can exacerbate existing migration or even initiate it in areas where fillers are initially well-placed.
The type of HA filler used also plays a role. Some fillers are formulated with varying crosslinking densities, which affect their cohesiveness and resistance to movement.
Highly crosslinked fillers tend to be more stable and less prone to migration compared to lightly crosslinked options.
Proper injection technique is essential for minimizing the risk of migration. Injecting the filler in a strategic manner, following anatomical landmarks, and avoiding overly aggressive or deep placements can help ensure the longevity and stability of the results.
Patients should be educated about potential risks associated with lip filler migration and advised to avoid habits that could contribute to it.
Regular follow-up appointments allow practitioners to monitor the filler’s placement and address any concerns promptly.
By understanding the interplay between movement, oral habits, and filler characteristics, both patients and practitioners can work together to achieve natural-looking, long-lasting lip enhancements while minimizing the risk of migration.
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Managing Lip Filler Migration: Prevention and Treatment Options
Choosing a Qualified Injector
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid fillers move from their intended placement within the lips. This can lead to an asymmetrical appearance, lumps, and an unnatural fullness in areas other than the desired location.
Several factors contribute to lip filler migration:
Fortunately, there are both preventive measures and treatment options available for managing lip filler migration:
Prevention:**
Treatment Options:**
Choosing a Qualified Injector:
Proper Injection Techniques
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid gel injected into the lips moves from its intended location.
Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
Preventing lip filler migration involves a combination of careful injection techniques and patient awareness:
If lip filler migration does occur, several treatment options are available:
Addressing Underlying Issues
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid fillers, injected into the lips, move from their intended location. This can result in an asymmetrical or uneven appearance, lumps, bumps, and distortion of lip contours. While generally a safe procedure, understanding the factors contributing to migration is crucial for both patients and practitioners.
Several factors can contribute to lip filler migration:
1. **Injection Technique:** Incorrect placement, excessive volume injection, or injecting too superficially can increase the likelihood of migration.
2. **Filler Type:** Different hyaluronic acid fillers have varying molecular weights and viscosities, influencing their stability. Some fillers are designed to be more resistant to migration.
3. **Patient Factors:** Certain patient characteristics, such as thin lips, excessive movement of facial muscles, or certain skin types, may make them more prone to filler migration.
4. **Lifestyle:** Activities involving significant facial muscle movements, like chewing, talking, smoking, and even kissing, can contribute to filler movement.
5. **Sun Exposure:** Ultraviolet radiation can degrade hyaluronic acid fillers, making them more susceptible to migration.
Preventing lip filler migration involves a multi-pronged approach:
1. **Choosing a Qualified Practitioner:** Selecting a skilled and experienced injector who understands anatomy and proper injection techniques is paramount.
2. **Pre-Injection Consultation:** A thorough assessment of individual patient factors, including facial movement patterns and skin type, should inform filler selection and placement.
3. **Appropriate Filler Choice:** Selecting a filler with appropriate viscosity and molecular weight for the desired area and patient characteristics is crucial.
4. **Careful Injection Technique:** Precise injection placement, avoiding overfilling, and using appropriate cannulas or needles can minimize migration risks.
5. **Post-Injection Instructions:** Adhering to post-injection care guidelines, such as avoiding excessive facial movement for the first few days and protecting the treated area from the sun, helps prevent filler displacement.
If lip filler migration occurs, treatment options exist:
1. **Dissolving the Filler:** Hyaluronidase, an enzyme, can be injected to break down hyaluronic acid fillers, allowing for removal and repositioning.
2. **Manual Redistribution:** In some cases, a skilled injector may manually redistribute the migrated filler to restore symmetry and contour.
3. **Massage Techniques:** Gentle massage of the treated area can sometimes help relocate displaced filler.
4. **Repeated Fillers:** In some situations, adding additional filler in strategic locations might be necessary to correct unevenness or asymmetry caused by migration.
Schedule a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige
Addressing underlying issues contributing to migration is essential for achieving lasting results. This may involve lifestyle modifications, such as reducing smoking and alcohol consumption, or addressing excessive facial muscle movement with Botox injections.
- Why CBD Gummies Are A Popular Option For Natural Pain Management - November 7, 2025
- What Is The Best Filler Technique For Nasolabial Folds? - November 6, 2025
- What Are The Benefits Of CBD Gummy Sweets For Pain Relief - November 4, 2025
