Arrange a Dermal Filler Consultation at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
Registration and Training Requirements
The registration and training requirements for Botox practitioners in the UK are regulated by the General Medical Council (GMC) and the British Association of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (BAAPS).
To work as a Botox practitioner, one must first complete a comprehensive training program that meets the standards set by these organizations.
- Training requirements typically involve completing a minimum of 100 hours of supervised clinical training with an experienced practitioner.
- This training should cover the basics of Botox injection technique, including patient selection and assessment, needle placement, and post-procedure care.
The training program also includes theoretical knowledge modules on topics such as:
- The pharmacology and mechanism of action of Botox
- Human anatomy and physiology relevant to injection sites
- Patient selection, risk assessment, and informed consent
- Needle safety and infection control
Additionally, trainees must also complete a series of exams to assess their knowledge and skills in these areas.
- The first exam tests the trainee’s understanding of Botox pharmacology and clinical use
- The second exam evaluates their ability to perform injections safely and effectively under supervised conditions
- The third exam assesses their understanding of patient care and post-procedure management
Once all the training requirements are met, trainees can apply for registration with the GMC.
- Registration involves meeting certain professional standards, including maintaining up-to-date knowledge of Botox technology and best practices
- Trainees must also commit to ongoing continuing professional development (CPD) to maintain their registration
In the UK, the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Edinburgh (RCS Ed) also provides certification for Botox practitioners through its Specialist Register.
- The certification process involves demonstrating expertise in a specific area of Botox use, such as facial rejuvenation or dystonia treatment
- Practitioners who achieve certification status demonstrate their commitment to staying up-to-date with the latest research and best practices in their chosen field
The Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons (APRAS) also offers Botox training programs for those seeking a broader understanding of facial aesthetics.
- APRAS-trained practitioners learn about advanced techniques and treatments using Botox, including fillers, chemical peels, and laser therapy
- The training emphasizes the importance of comprehensive treatment planning and collaboration with other healthcare professionals as needed
By completing these comprehensive training programs and meeting registration requirements, practitioners can demonstrate their commitment to providing high-quality care for patients undergoing Botox treatments.
The General Medical Council (GMC) is the regulatory body responsible for ensuring that healthcare professionals, including practitioners of cosmetic treatments such as Botox, meet certain standards of education and training.
As part of its regulatory framework, the GMC requires all practitioners who wish to offer cosmetic treatments, including Botox, to complete a series of training modules. These modules are designed to equip practitioners with the necessary knowledge and skills to provide safe and effective treatments.
The training requirements are outlined in the GMC’s guidance document, “Guidance on the Training Requirements for Practitioners who administer Botulinum Toxin (BTX) for Cosmetic Purposes”.
Practitioners must complete a minimum of 5 hours of core training, which covers essential topics such as:
- The use and risks associated with Botox
- The anatomical structures that can be affected by Botox
- The principles of Botox administration, including the correct injection technique and safety measures
- The risks and complications associated with Botox treatment, including side effects and adverse reactions
- The importance of informed consent and patient communication in cosmetic medicine
In addition to the core training, practitioners must also complete a further 2-3 hours of refresher training every 5 years. This refresher training is designed to ensure that practitioners stay up-to-date with the latest developments and best practices in cosmetic medicine.
The GMC also requires practitioners to maintain a record of their training and continuing professional development (CPD). This includes keeping a logbook of all their training hours, which must be available for inspection by the GMC or other regulatory bodies on request.
Practitioners who fail to meet the GMC’s training requirements may face regulatory action, including fines and disciplinary proceedings. The GMC takes the safety of patients seriously and will not tolerate any practitioner who is found to be inadequately trained or inexperienced in providing cosmetic treatments.
In summary, the GMC requires all practitioners of cosmetic treatments, including those who administer Botox, to complete a series of training modules that cover essential topics such as the use and risks associated with Botox, anatomical structures, principles of administration, risks and complications, informed consent, and patient communication.
The training requirements for Botox practitioners in the UK are regulated by the General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC) and the British Association of Cosmetic Nurses (BACN), among other organizations. To become a qualified practitioner, one must undergo comprehensive training that covers various aspects of Botox administration, including its uses, side effects, and contraindications.
Typically, this training involves both theoretical and practical components. Theoretical components cover the medical ethics surrounding Botox use, patient assessment techniques, and treatment planning. Medical ethics are a crucial aspect of Botox practice, as practitioners must consider factors such as informed consent, confidentiality, and potential complications.
During the training phase, practitioners learn about the different types of Botox, their indications, and how to evaluate patients for suitability. They also study patient assessment techniques, including how to evaluate facial anatomy, identify potential risks and benefits, and determine the best treatment plan for each individual.
The practical component of the training typically involves hands-on experience with Botox administration under the supervision of experienced practitioners. This allows candidates to gain the necessary skills and confidence to perform procedures on patients in a clinical setting.
Additionally, many training programs require participants to complete modules or workshops that focus on specific aspects of Botox practice, such as treatment administration, complications management, and patient aftercare.
In the UK, it is mandatory for all practitioners who administer Botox to be registered with the GPhC. To meet this requirement, candidates must pass a series of exams that assess their knowledge and understanding of pharmacology, ethics, and practice standards.
The training period typically lasts several months to a year or more, depending on the individual’s prior experience and qualifications. Throughout the process, candidates are monitored and assessed regularly to ensure they meet the required standards.
Once certified, practitioners must complete continuing professional development (CPD) requirements to maintain their registration. This ensures that they stay up-to-date with the latest developments in Botox practice, including new techniques, technologies, and guidelines.
In summary, becoming a qualified Botox practitioner in the UK requires comprehensive training that covers medical ethics, patient assessment, treatment administration, and other essential topics. By meeting these requirements, practitioners can gain the necessary skills, knowledge, and confidence to provide safe and effective care for their patients.
Gaining the required training to administer Botox injections is crucial for any practitioner looking to work in the field. In the UK, the General Medical Council (GMC) sets out the standards that must be met by practitioners wishing to work with medical substances like Botox.
-
Arrange a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
- Practitioners must undergo a minimum of 2 days of training before being allowed to administer Botox on their own in clinical practice. This training should include both theoretical and practical components, covering topics such as the anatomy of the face, the action of botulinum toxin, and the principles of Botox injections.
- The training program must be delivered by a recognized body, such as the British Association of Cosmetic Nurses (BACN) or the General Dental Council (GDC). These bodies ensure that the training meets the GMC’s standards and provides practitioners with the necessary knowledge and skills to administer Botox safely.
- During the initial training period, practitioners will be expected to complete a minimum of 20-25 hours of learning time. This includes both classroom instruction and hands-on practice under the supervision of experienced trainers.
- After completing their initial training, practitioners must also complete a series of assessment exercises to demonstrate their competence in administering Botox injections. This may include written exams, practical assessments, or both.
It’s worth noting that some employers may require additional training or experience beyond what is mandated by the GMC. For example, a practitioner working in a private clinic may need to complete ongoing refresher courses to maintain their skills and knowledge.
The GMC also recommends that practitioners undergo regular refresher courses to maintain their skills and knowledge. These courses should be delivered by recognized bodies and cover topics such as new techniques, emerging trends, and changes to existing practices.
- Practitioners must complete a minimum of 1 hour of continuing professional development (CPD) per year to meet the GMC’s requirements.
- The CPD should be relevant to the practitioner’s area of work and include topics such as Botox injections, facial anatomy, patient assessment, and aftercare procedures.
- Practitioners must also demonstrate that they have access to up-to-date information on best practice and that they are aware of any changes to laws, regulations, or industry standards.
In summary, gaining the required training to administer Botox injections in the UK involves completing a minimum of 2 days of training with a recognized body, followed by assessment exercises and ongoing CPD. By meeting these requirements, practitioners can ensure that they are providing safe and effective treatments for their patients.
Licensing and Accreditation
Licensing and accreditation are crucial aspects to consider when it comes to providing safe and effective treatments like Botox in the UK.
In the UK, Botox is considered a medical treatment, therefore, practitioners must obtain the necessary qualifications and certifications to administer it safely and correctly.
The General Medical Council (GMC) regulates medical professionals in the UK, including those who provide aesthetic treatments like Botox.
According to the GMC, anyone wishing to offer Botox treatments must demonstrate that they have sufficient knowledge, skills, and experience to do so safely and effectively.
This is typically achieved by completing a recognized training program approved by the GMC or other relevant regulatory bodies, such as the British Association of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons (BASAPS).
The training typically covers a range of topics including Botox pharmacology, anatomy, and administration techniques, as well as risk management and emergency procedures.
Some popular training programs for Botox practitioners in the UK include those offered by BASAPS, the British Association of Cosmetic Nurses (BACN), and the National Institute for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Management (NICDPM).
In addition to formal training, many UK-based clinics require practitioners to complete a safe injection technique course, such as the one offered by Allergan (the manufacturer of Botox) or another recognized provider.
These courses teach practitioners how to safely inject Botox using a sterile technique, which minimizes the risk of complications and ensures that patients receive the best possible treatment outcomes.
Safe injection training typically covers topics such as patient selection, skin preparation, needle insertion techniques, and post-procedure care.
Some clinics may also require practitioners to complete additional training in areas such as facial anatomy, relaxation techniques, or pain management.
BASAPS recommends that all practitioners providing Botox treatments should have completed a minimum of 20 hours of training, which covers both the theoretical and practical aspects of Botox administration.
Clubs like BASAPs offer extensive accreditation in areas such as safe injection, facial anatomy and more for practitioners who wish to become certified in treating patients with Botulinum Toxin products including Botox
In the UK, some clinics may also require practitioners to demonstrate proficiency in using a range of equipment, such as ultrasound devices or Botox delivery systems.
This is often achieved through additional training programs or on-the-job experience under the supervision of an experienced practitioner.
Licensing and Accreditation are crucial aspects to consider when it comes to **Practitioner** training, especially in fields like cosmetic treatments such as _Botox_.
In the UK, regulatory bodies require practitioners to undergo extensive education and training to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform procedures safely and effectively.
Accreditation is a process by which an organization or institution verifies that its programs or courses meet certain standards of quality. In the context of _Botox_ practitioners, accreditation typically involves meeting specific requirements set forth by governing bodies such as the General Medical Council (GMC) or the Care Quality Commission (CQC).
Furthermore, practitioners must complete comprehensive training programs, including modules on **Pharmacology**, **Anatomy**, and **Surgical Techniques**. This ensures that they have a thorough understanding of the treatment, its benefits, and potential risks.
Safe injection practices are also an essential component of _Botox_ practitioner training. This includes learning about *_Aseptic Techniques_*, proper needle handling, and anatomical landmarks to minimize complications.
*_Complications_* such as bruising, swelling, or nerve damage can arise from improper technique or equipment use. Practitioners must be educated on how to recognize these potential issues and take steps to prevent them.
In addition to technical skills, practitioners should also receive training in patient assessment and counseling. This includes understanding patient medical histories, allergies, and other relevant factors that may impact treatment decisions.
Finally, _Botox_ practitioners must stay up-to-date with the latest research and developments in the field through ongoing education and professional development opportunities.
By adhering to licensing and accreditation standards, ensuring proper training, and maintaining continuous education, _Botox_ practitioners can provide safe and effective treatment for their patients, while minimizing the risk of complications and adverse outcomes.
Licensing and accreditation play a crucial role in ensuring that training programs provided to Botox practitioners in the UK meet the required standards. In the UK, the regulation of medical aesthetics is overseen by the General Medical Council (GMC) and the Care Qualities Framework (CQF), which sets out the requirements for accredited training providers.
Accredited training programs are provided by universities such as the University of Manchester and the Royal Society of Medicine (RSM), who have been approved by the GMC to offer training in medical aesthetics. These institutions have undergone a rigorous process of accreditation, which involves meeting specific standards set out by the GMC, including ensuring that their training programs are of high quality, relevant, and effective.
The GMC requires that accredited training providers have a clear understanding of the requirements for safe and effective use of Botox, as well as the necessary knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. The training program must also cover the administration and management of potential complications, such as bruising or eyelid drooping.
Accredited training programs typically include both theoretical and practical components, which provide participants with a comprehensive understanding of Botox and its applications. Participants may gain hands-on experience by practicing procedures on mannequin heads or other models under the supervision of experienced practitioners.
The RSM is also involved in regulating medical aesthetics in the UK, and it offers its own accreditation for training programs in this field. The RSM’s accreditation process involves assessing the quality of the training program against strict standards, including ensuring that participants are adequately trained in the safe use of Botox and other medications.
In addition to licensing and accreditation, healthcare professionals must also meet the requirements of their professional regulatory bodies, such as the GMC or the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC). These organizations have their own standards for training and competence in medical aesthetics, which are separate from those set out by the GMC.
For example, to practice Botox in the UK, a practitioner must be registered with the HCPC as an independent prescribing nurse or doctor. This requires completing a training program accredited by the RSM or another approved organization and meeting the necessary standards of competence.
The importance of licensing and accreditation for Botox practitioners cannot be overstated. It ensures that participants receive high-quality training, which equips them with the knowledge and skills needed to provide safe and effective treatments for patients.
Professional Development
To maintain and enhance their skills, Botox practitioners in the UK are required to engage in regular continuing professional development (CPD). CPD is essential for professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest techniques, technologies, and industry developments.
The General Medical Council (GMC) and the British Association of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons (BAAPS) recommend that doctors, including Botox practitioners, participate in ongoing training and education to ensure they provide high-quality care to their patients.
CPD for Botox practitioners in the UK typically involves:
- Attending conferences, seminars, and workshops related to aesthetics and botulinum toxin treatments
- Presenting at industry events or contributing to publications
- Completing online training modules or courses
- Participating in peer review and quality assurance programs
- Staying up-to-date with the latest research and clinical guidelines on Botox and other aesthetic treatments
The frequency of CPD activities can vary depending on the individual practitioner’s circumstances. However, it is generally recommended that Botox practitioners engage in regular training and education to stay current with best practices and industry developments.
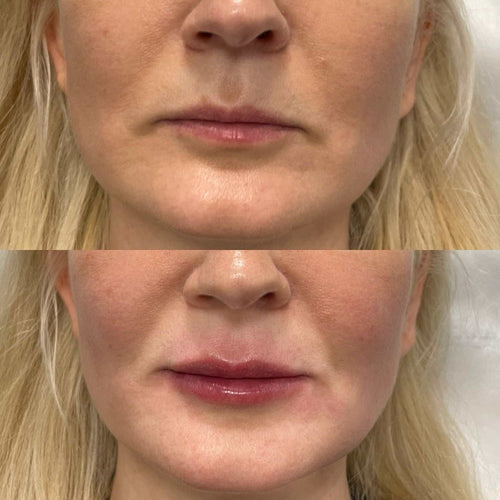
Some common CPD topics for Botox practitioners in the UK include:
- The latest techniques and technologies in Botox treatments
- New indications and off-label uses for Botox
- Patient safety and risk management
- Product updates and formulation changes
- Business and marketing strategies for aesthetic practitioners
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Consult Dr. Laura Geige

In addition to formal training programs, CPD activities can also include:
- Mentorship and coaching from experienced practitioners
- Peer-to-peer learning and discussion groups
- Online forums and communities focused on aesthetics and Botox treatments
- Self-study and reading of industry publications and research papers
The benefits of CPD for Botox practitioners in the UK are numerous:
- Improved patient outcomes and safety
- Enhanced professional credibility and reputation
- Staying up-to-date with industry developments and advancements
Certainly, CPD is a critical aspect of maintaining and enhancing one’s skills as a Botox practitioner in the UK. By engaging in regular training and education, practitioners can ensure they provide high-quality care to their patients while also staying competitive in the industry.
In order to maintain their license to practice, practitioners must complete regular Continuing Professional Development (CPD) courses. This is a crucial aspect of staying up-to-date with the latest techniques and best practices in the field.
CPD requirements for Botox practitioners in the UK vary depending on the regulatory body and the type of treatment being offered. However, most professional associations, such as the British Association of Cosmetic Physicians (BACP) and the British Medical Acupuncture Council (BMAC), require members to complete a certain number of hours of CPD per year.
The CPD requirements typically include courses on topics such as advanced Botox techniques, patient care, and related areas such as fillers, chemical peels, and laser treatments. These courses are designed to help practitioners stay current with the latest research, technologies, and best practices in the field.
- Courses may also cover business skills and practice management, as well as topics such as patient confidentiality and data protection.
- Practitioners must ensure that their CPD is relevant to their specific role and that it aligns with the regulatory requirements for their profession.
- A minimum number of hours of CPD may be required before a practitioner can renew their license or certification.
Examples of courses that may be included in a Botox practitioner’s CPD program include:
- Advanced Botox techniques, such as off-label uses and novel injection methods
- Patient care courses, focusing on topics such as consent forms, aftercare instructions, and patient engagement
- Courses on fillers, chemical peels, and other treatments often used in conjunction with Botox
- Business skills courses, covering topics such as marketing, finance, and practice management
- Courses on related areas, such as medical law, data protection, and patient confidentiality
The importance of CPD cannot be overstated. Not only does it help practitioners stay current with the latest techniques and best practices in the field, but it also demonstrates their commitment to ongoing learning and professional development.
The British Association of Cosmetic Nurses (BACN) plays a significant role in providing high-quality training and education to cosmetic nurses and practitioners in the UK, particularly those who administer non-surgical treatments like Botox.
One of the key ways that BACN supports the professional development of its members is through the offering of accredited Continuing Professional Development (CPD) courses.
The CPD courses are designed to be engaging, informative, and relevant to the needs of cosmetic nurses and practitioners in the UK, with a focus on current best practices, research, and industry developments.
These courses are typically delivered through a combination of online learning modules, face-to-face workshops, and lectures, allowing participants to choose the format that suits them best.
BACN’s CPD courses cover a wide range of topics, including but not limited to: Botox administration techniques, skin anatomy, facial anatomy, botulinum toxin management, and advanced aesthetics treatments such as fillers, chemical peels, and laser therapy.
The association also provides access to its online library, which contains a vast repository of educational resources, including e-books, videos, webinars, and other digital content related to cosmetic nursing and Botox administration.
Furthermore, the BACN CPD courses are recognized by many UK healthcare employers as being relevant to their training requirements for cosmetic nurses and practitioners, which can enhance job prospects and career advancement opportunities.
Additionally, members of the BACN who complete a certain number of hours of CPD throughout the year will receive a certificate of completion that confirms their ongoing professional development commitment, demonstrating to employers and clients that they are up-to-date with the latest knowledge and skills in cosmetic nursing.
The accreditation offered by BACN is also recognized by the General Medical Council (GMC) and the UK’s Professional Standards Authority for Regulated Professions (PSA), which can help to enhance credibility and trustworthiness among employers and clients.
Overall, the CPD courses offered by the British Association of Cosmetic Nurses represent an essential investment in the ongoing professional development of cosmetic nurses and practitioners in the UK, helping them to stay up-to-date with the latest knowledge and skills in Botox administration and other areas of cosmetic nursing.
Read more about James Martin Live here. Read more about Otherwheres Magazine here. Read more about Ring of the Reeks Cycle here. Read more about Prince and Flower here. Read more about Highland Spring Magazine here.
- Why CBD Gummies Are A Popular Option For Natural Pain Management - November 7, 2025
- What Is The Best Filler Technique For Nasolabial Folds? - November 6, 2025
- What Are The Benefits Of CBD Gummy Sweets For Pain Relief - November 4, 2025
